Greece – Attica, Mesogia
Location: Attica, Mesogia, Greece
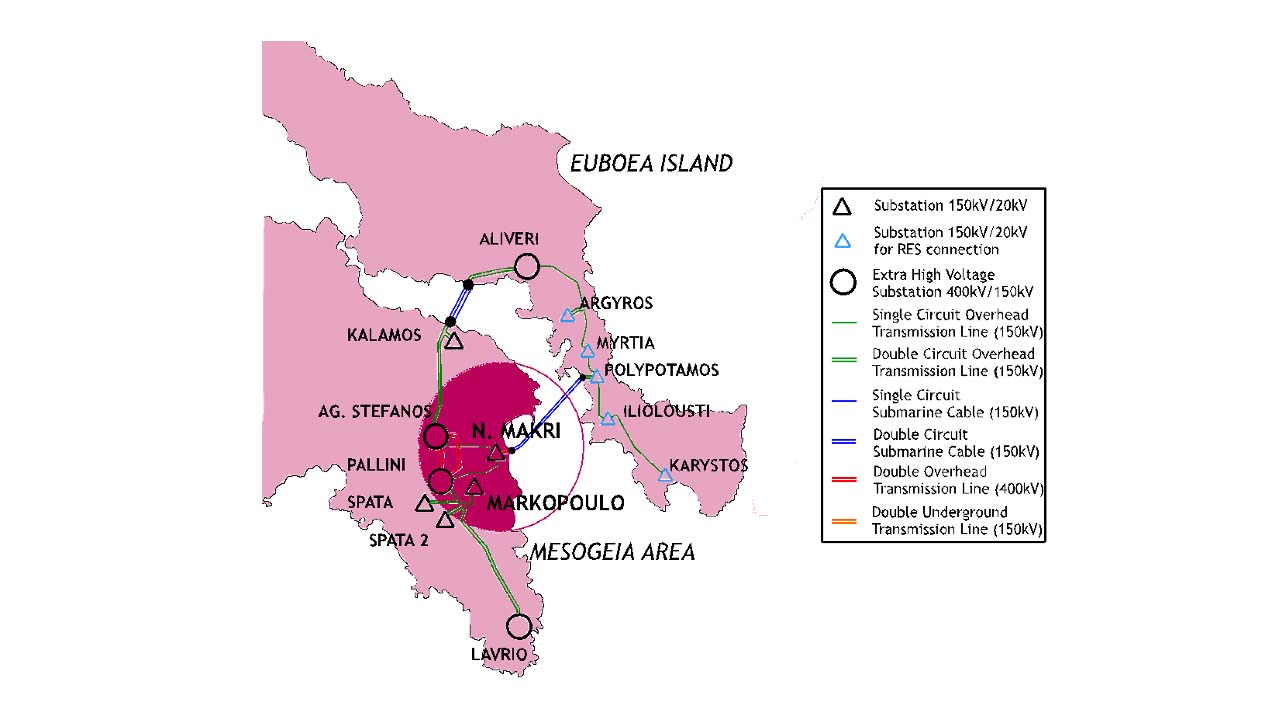
The Greek pilot will mostly take place in the Mesogia Area, located in the Attica region of central Greece, which places it at the outskirts of the Athenian metropolis. Mesogia area includes the municipalities of Koropi, Lavrio, N. Makri and the interconnected islands of Kea, Andros and Tinos. It has been the pilot site for several Horizon 2020 and Europe projects, including Coordinet, Platone and, now, EV4EU. It is a semi-rural area that includes approximately 225,000 customers in its Low-Voltage (LV) and Medium-Voltage (MV) networks, varied from households to small, medium, and large industries. The area benefits from installations of various forms of renewables, wind farms, and PV, including net metering and rooftop PVs as well.
One of the sections, the distribution network of Markopoulo, consists of several voltage feeders (20 kV) connected to three HV/MV transformers with a 50 MVA capacity. Concerning RES penetration, there are 27.043 MW of PV plants connected to the Distribution Network. In addition, there are 20.7 MW of PV plants under approval for connection on the Distribution Network. There are no Wind farms connected to the Distribution Network.
The main aspects of the Greek demo are the deployment and testing of the Open V2X management platform for public chargers, developed by PPC, the integration and testing of the flexibility algorithms for local and system-wide grid services developed by DTU and INESC-ID, and the investigation of exploitation and marketability strategies for the proposed solutions with the contribution of CITROËN.
4 Use- Cases (UC) will be tested in the Greek Demonstrator:
- Open V2X Management Platform
Testing the platform as a software tool. The O-V2X Management Platform, developed in WP5 under the leadership of PPC, will be completed and tested. The tests will include new EV integration methodologies which require platform involvement, interoperability, and communication issues with end-devices, such as chargers, and user interface. PPC has an R&D campus near the Mesogeia Area (Kantza, Athens), the Innovation Hub, where proof-of-concept scenarios of the V2X platform will be conducted.
- New Demand Response and Flexible Capacity Contracts
Smart EV methodologies and impact on the grid and public charging operation. This UC will validate the EV integration methodologies that are part of the Greek demo, such as DR, flexible capacity contracts, market services, Green Charging, etc. Topics of interest are the impact on the distribution network, on the Public Charging operation of PPC and feasibility issues related to implementation of this method in cooperation with the O-V2X platform.
- V2X management by Charging Point Operator (CPO)
Platform and integration with users and other end devices. The platform will be tested in cooperation with all user and other end-devices from the field, such as public chargers, etc. The scope in these tests is to identify efficient mechanisms for electric vehicle charging and discharging, that is also connected with the actual final scope of the demo. These mechanisms are closely connected with standardization activities of the Open Charge Alliance (OCP), such as the Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP). Finally, the V2X platform integrated functionalities will be also tested in the field. KPIs collected from these tests include interoperability and communication metrics, activation success and user responsiveness, among others.
- Activation of V2X services by Distribution Services Operator (DSO)
Platform and DSO- Full integration – Interoperability. In this UC, the integration of the platform with the DSO systems and operation will be accomplished, and the methodologies of the Greek demo will be tested in the field and/or in realistic validation environment. The objective is to assess the proposed solution across its operational chain, i.e., interoperability issues (including with DSO systems), user response, effect on the distribution network safe operation, contribution to flexibility management required by the DSO.